Inter- and Intra-Series Embeddings Fusion Network for Epidemiological Forecasting
Feng Xie, Zhong Zhang, Xuechen Zhao, Bin Zhou and Yusong Tan
Published in The 34th International Conference on Software Engineering & Knowledge Engineering (SEKE2022)
Abstract
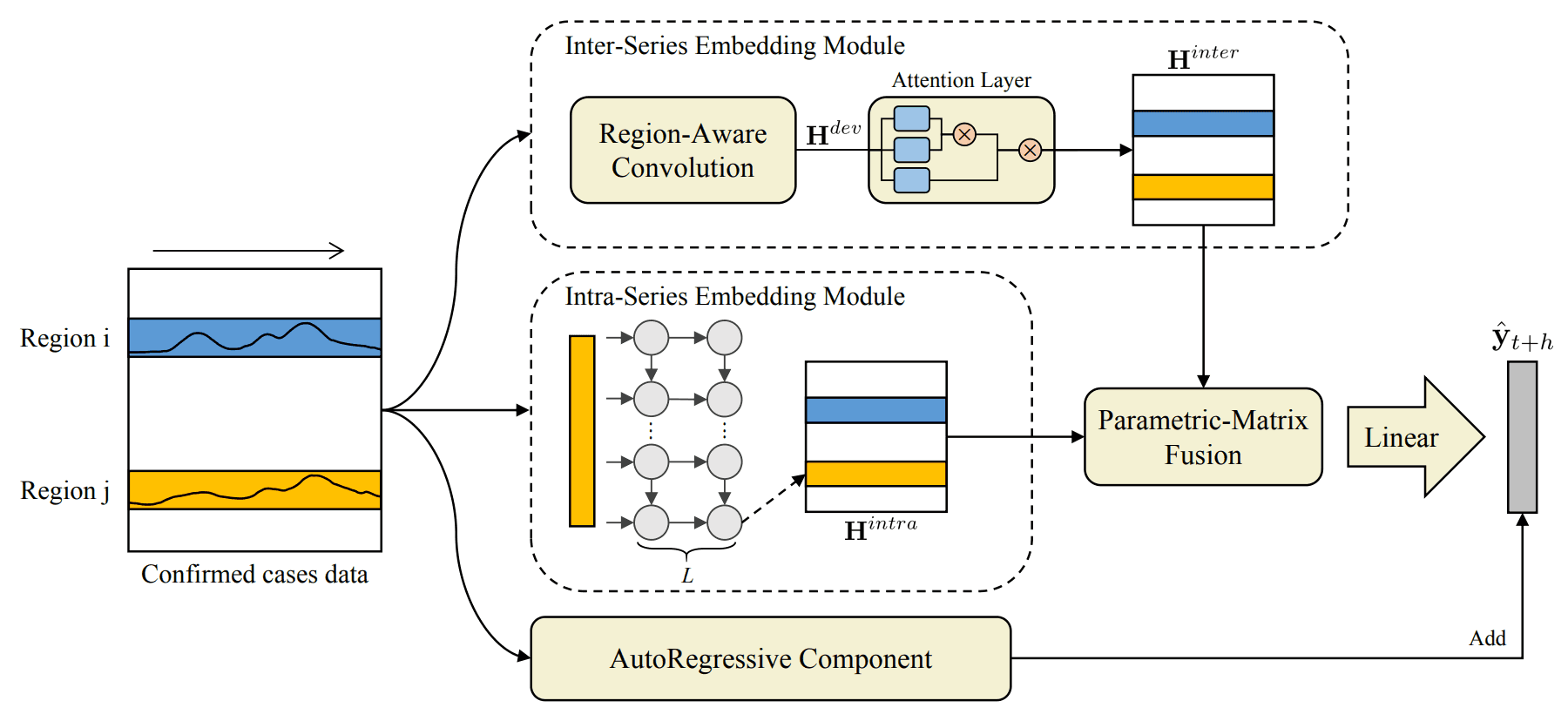
The accurate forecasting of infectious epidemic diseases is the key to effective control of the epidemic situation in a region. Most existing methods ignore potential dynamic dependencies between regions or the importance of temporal dependencies and inter-dependencies between regions for prediction. In this paper, we propose an Inter- and Intra-Series Embeddings Fusion Network (SEFNet) to improve epidemic prediction performance. SEFNet consists of two parallel modules, named Inter-Series Embedding Module and Intra-Series Embedding Module. In Inter-Series Embedding Module, a multi-scale unified convolution component called Region-Aware Convolution is proposed, which cooperates with self-attention to capture dynamic dependencies between time series obtained from multiple regions. The Intra-Series Embedding Module uses Long Short-Term Memory to capture temporal relationships within each time series. Subsequently, we learn the influence degree of two embeddings and fuse them with the parametric-matrix fusion method. To further improve the robustness, SEFNet also integrates a traditional autoregressive component in parallel with nonlinear neural networks. Experiments on four real-world epidemic-related datasets show SEFNet is effective and outperforms state-of-the-art baselines.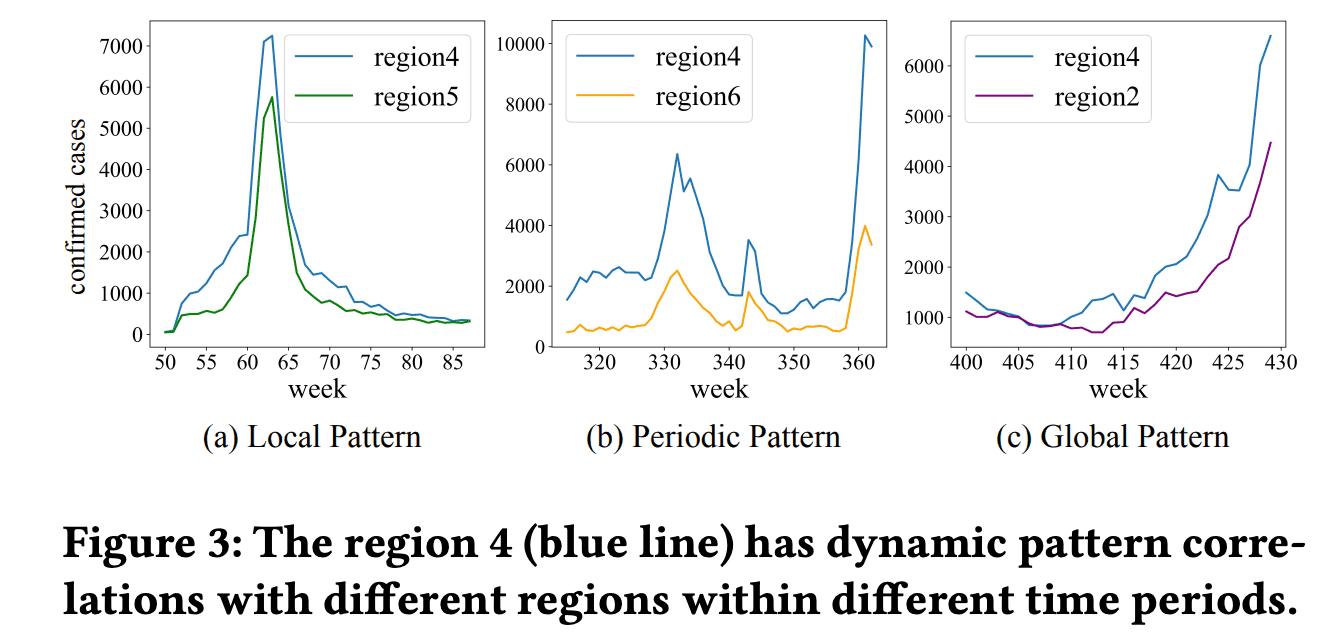

Main Contributions
- We propose a new model that extracts inter-series correlations and intra-series temporal dependencies through two separate neural networks and uses parametric-matrix fusion to emphasize the importance of each information for epidemic prediction.
- We propose a multi-scale unified convolution component called Region-Aware Convolution that is capable of extracting local, periodic, and global patterns to better obtain feature representation and capture potential dependencies between regions.
- We conduct extensive experiments on four real-world epidemic-related datasets. The results show that our model achieves better performance than other state-of-the-art methods and demonstrates the effectiveness of each component.

Experiments
We conduct experiments on four epidemic-related datasets, three are seasonal influenza datasets and one are COVID-19 datasets. More about the experimental results, please refer to the paper.
